Pathology
For a review of the pathology of FTD read this paper from our team and their collaboration with the Queen Square Brain Bank.

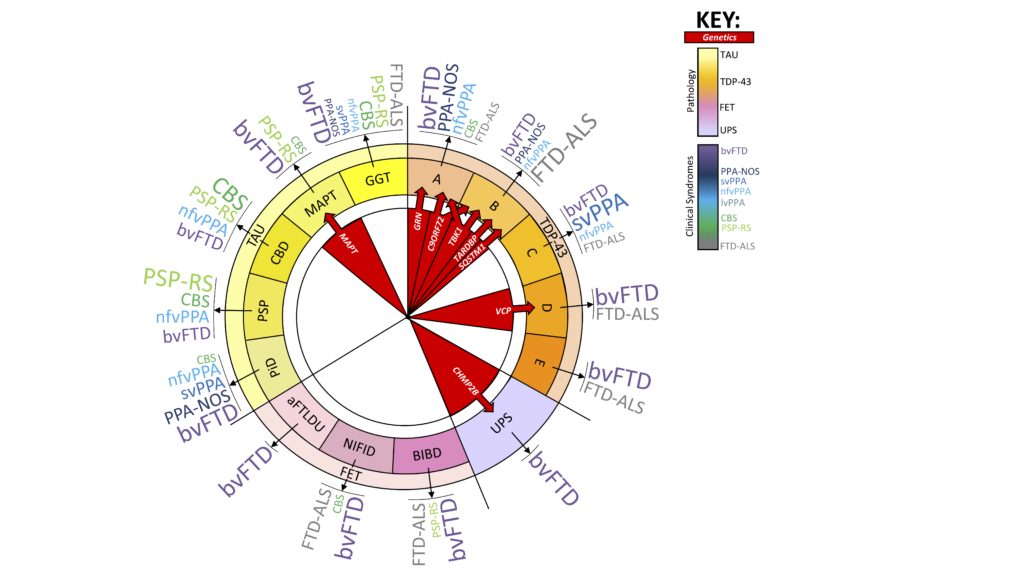
At post mortem proteins are found clumped in an abnormal way in brain cells in FTD. There are three key proteins which are called tau, TDP-43, and FUS, and together they are known as frontotemporal lobar degeneration or FTLD pathology.
Most brain banks report that about 45-50% of people have TDP-43 or FTLD-TDP pathology, 40-45% have tau or FTLD-tau pathology, and 5-10% have FUS or FTLD-FUS pathology. A very small number of people with FTD have none of these and this group includes those with CHMP2B mutations.
Each of the three proteins can be found clumped in different patterns, which each have a name.
For tau the subtypes are called :
- Pick’s disease
- corticobasal degeneration or CBD
- progressive supranuclear palsy or PSP
- argyrophilic grain disease or AGD
- globular glial tauopathy or GGT
- the pathology seen in people with mutations in the MAPT or tau gene
- neurofibrillary tangle disease or NTD
The non-tau forms of FTLD used to be called FTLD-U or ubiquitin-positive, tau-negative pathology. The majority of this group are those with TDP-43 pathology who are subdivided into:
- type A – including those with GRN mutations and some people with C9orf72 expansions
- type B – including some people with C9orf72 expansions
- type C
- type D – including those with VCP mutations
- type E
Subtypes of FTLD-FUS are:
- atypical FTLD with ubiquitin inclusions or aFTLDU
- neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease or NIFID
- basophilic inclusion body disease or BIBD
There is no clear one to one association of a clinical syndrome with a particular pathology:
- BvFTD is the most heterogeneous of the clinical syndromes and can be caused by any of the pathologies.
- SvPPA is usually caused by TDP type C.
- NfvPPA is associated mainly with tau pathology, usually CBD, PSP or Pick’s disease, but can also be associated with TDP pathology, usually types A or B.
- LvPPA is almost always caused by Alzheimer’s disease pathology rather than FTLD.
- CBS is caused mainly by tau pathology, but is only associated with CBD in about 30-50% of people. Other tau pathologies includes PSP, Pick’s disease and MAPT mutations. About 20-30% of people with CBS have Alzheimer’s disease pathology, and about 10% have TDP-43 pathology, usually type A.
- The PSP clinical syndrome is almost always caused by PSP pathology.
- FTD-MND is usually associated with TDP-43 pathology, commonly type B.
A summary of the different associations between the clinical syndrome and the type of pathology can be found in the picture below: